PATIENT EDUCATION:
COMMON RETINAL DISORDERS:
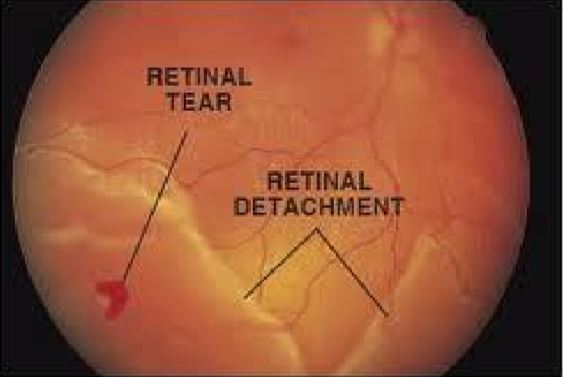
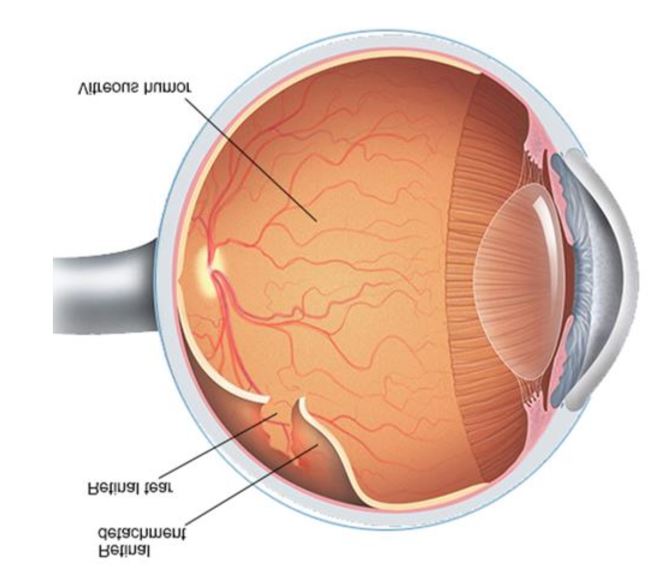
- Retinal Tear – Tears are due to a flap of retina being pulled off the choroids as the vitreous
shrinks - Retinal Hole – Holes are circular defects in the retina
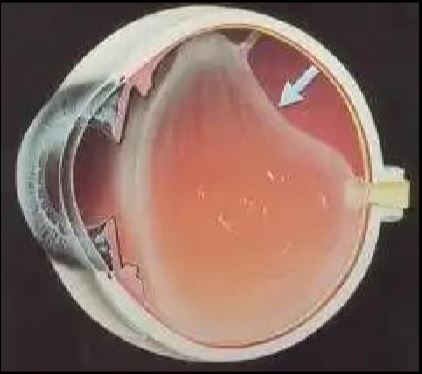
- Retinal Detachment (RD) – Separation of retina from the back wall of the eye
- Lattice degeneration
- Retinal hole or tear
- Injury
- Long term diabetes mellitus
- Myopia
- Spontaneous i.e. without any obvious cause
- Surgery is the only possibility for treating retinal detachment
Diabetes is caused by increased sugar level in the blood
The long term effects are on eyes, kidneys, nerve, skin & heart
- Longstanding Diabetes Mellitus damages the small blood vessels of the retina, which normally supply
- Oxygen to the retina and thus keep it alive
- These damaged vessels either leak or close down
- However these new blood vessels are fragile and not well formed. Thus these are of little help, rather they pose a constant threat of bleeding at any time leading to severe sight threatening complications
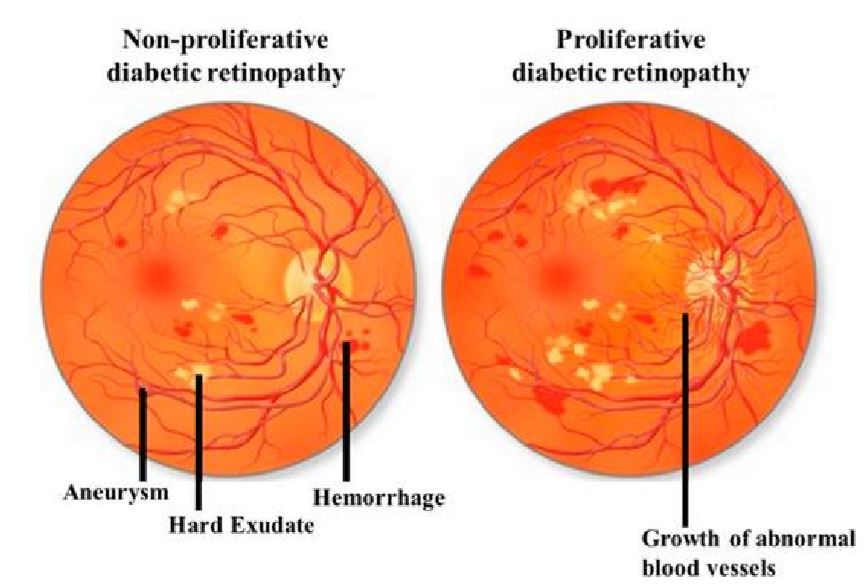
- If the leakages occur in the central part of the retina called macula, it leads to loss of central vision Closure leads to oxygen starvation of the retina, which finally leads to formation of abnormal new vessels to try and improve oxygen supply
- However these new blood vessels are fragile and not well formed. Thus these are of little help, rather they pose a constant threat of bleeding at any time leading to severe sight threatening complications
- Background Diabetic Retinopathy
- Initial stage of Diabetic Retinopathy
- Pre-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
- High Blood Pressure
- Pregnancy
- Smoking
If diabetic retinopathy is noted, colour photographs of the retina may be taken and FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY performed. This involves dilating the pupils and injection of a fluorescent dye into a vein in the arm. Photographs of the retina are taken rapidly as the dye passes through the retinal blood vessels. This test helps in determining if laser photocoagulation treatment is necessary. If treatment is to be done, it helps in identifying what structures and areas need treatment with laser.
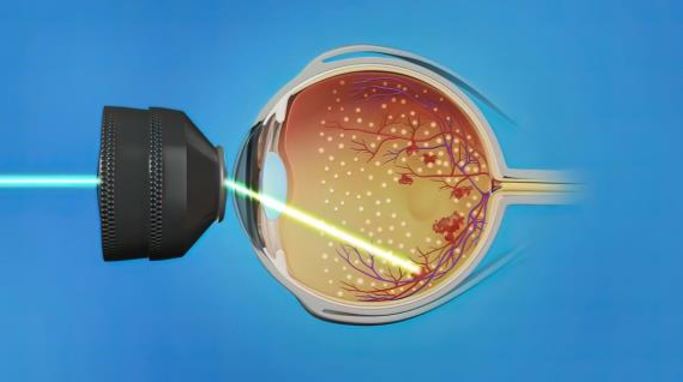
PHOTOCOAGULATION involves the use of a LASER beam to seal leaking blood vessels and prevent growth of abnormal blood vessels. This procedure does not require hospitalization. In background retinopathy, if blood vessels are leaking fluid into the macula, laser treatment stops the leakage and may improve or stabilize vision.
In proliferative retinopathy, laser treatment may involve one or more sessions depending on the type or severity of retinopathy. Laser treatment significantly reduces the chances of severe visual loss by destroying the abnormal blood vessels and preventing growth of more such vessels. Vision may improve or stabilize within several weeks to a year. It is important to remember that laser treatment is not a one-time procedure. Regular follow-up is extremely important. Your doctor will tell you when to return for a check-up.
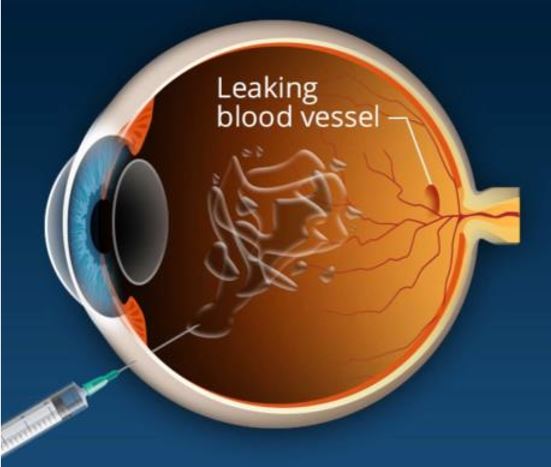
Recently, along with laser treatment, certain medication when injected into the eye or just outside the eye has shown encouraging results. These include anti-VEGF agents such as Avastin, Lucentis and Macugen. They act by reducing macular edema i.e. the swelling in the retina as well as inhibiting growth of abnormal new vessels, or by reducing bleeding from new vessels which may be refractory to conventional laser treatment.
Another agent used is the steroid Triamcinolone Acetonide. This can be either injected into the eye (intravitreally) or into the side of the eye (Sub-Tenons). This agent works well for diabetic macular edema (swelling). However, increase in eye pressure and increased incidence of cataract, are potential side effects. These medicines should therefore be used cautiously and judiciously.
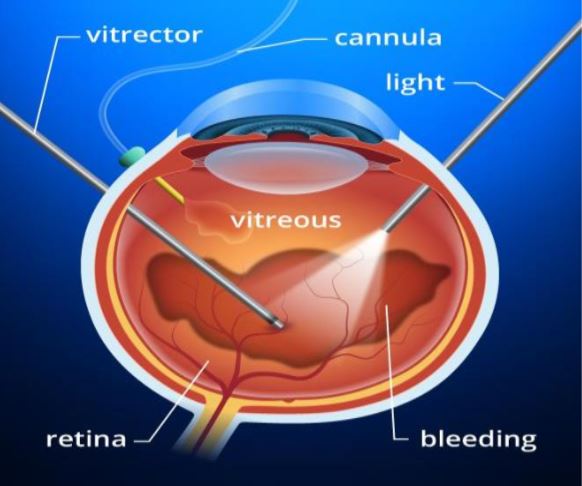
If the vitreous is too clouded with blood or there is traction retinal detachment, laser treatment will not work. In this situation, a surgical procedure called VITRECTOMY needs to be performed. In this operation, opaque vitreous gel is removed from within the eye by a special instrument that simultaneously sucks and cuts the vitreous.
Membranes on the retina which are responsible for traction and recurrent bleeding are dissected. More complete photocoagulation can then be carried out. In case of retinal detachment due to traction in severe cases, gas or silicone oil tamponade is paced at the end of the procedure.